Wi-Fi IoT Protocol/connectivity is usually a clear choice for several developers because it’s fast wireless and supply hassle-free connectivity,
WiFi stands for (WiFi full form) Wireless Fidelity/ frequencies which enable the interconnectivity of the many computers hence how to attach internet from the access point to the pc or laptop.
We all realize Wifi actually,many of you would possibly be using it now to read this blog.It allows to access the web while on the move.Wi-Fi enabled computers send and receive data indoors and out.Its even as fast as cable modem connection.It refers to the IEEE 802.11 communications standard.It usually establishes an area Area Network(LAN).
WiFi connectivity is usually a clear choice for several developers, especially given the pervasiveness of WiFi within the house environment within LANs. It requires little further explanation except to state the apparent that clearly there’s a good existing infrastructure also as offering fast data transfer and therefore the ability to handle high quantities of knowledge .
Currently, the foremost common WiFi standard utilized in homes and lots of businesses is 802.11n, which offers serious throughput within the range of many megabit per second, which is ok for file transfers, but could also be too power-consuming for several IoT applications. A series of RF development kits designed for building WiFi-based applications are available from RS.
• Standard: supported 802.11n (most common usage in homes today)
• Frequencies: 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands
• Range: Approximately 50m
• Data Rates: 600 Mbps maximum, but 150-200Mbps is more typical, counting on channel frequency used and number of antennas (latest 802.11-ac standard should offer 500Mbps to 1Gbps)
• The role of WiFi within the IoT space is usually overlooked. WiFi is compatible to support certain IoT applications that need high bandwidth and low latency.
Wireless LAN:
• It uses high frequency radio waves instead of wires to speak and transmit data.
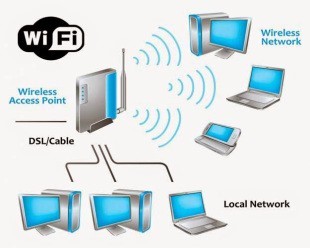
• An Access Point connects wired and wireless networks together and enables the sending and receiving of knowledge between wireless clients and therefore the wired network.
• The wireless SSID, also referred to as the ‘Network Name’, is that the Service Set Identification controls access to a given wireless network.
WIFI in OSI Model:
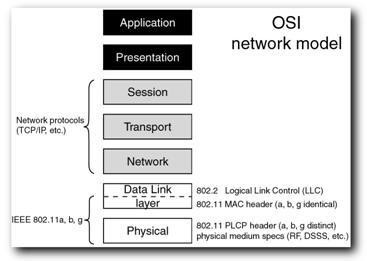
As we will see in image above,Wifi belongs to both Layer1(Physical) and Layer2(Data Link).
Advantages and drawbacks of Wifi:
Advantages:
• Frees network devices from cables
• Cheaper development for embedded system
• Reliable products
• Security
• High speed
Disadvantages:
• 802.11b/g use the two .4 GHz spectrum, which is crowded with other devices (Bluetooth… )
• 802.11n doubles the radio spectrum/bandwidth (40 MHz)
• Power consumption
• Limited network range
• Security risks (configuration)
Summary:
Currently, the foremost common Wi-Fi standard utilized in homes and lots of businesses is 802.11n, which offers serious throughput within the range of many megabit per second, which is ok for file transfers but maybe too power-consuming for several IoT applications.
o Standard: supported 802.11n (most common usage in homes today)
o Frequencies: 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands
o Range: Approximately 50m
o Data Rates: 600 Mbps maximum, but 150-200Mbps is more typical, counting on channel frequency used and number of antennas (latest 802.11-ac standard should offer 500Mbps to 1Gbps)
—



Like!! Really appreciate you sharing this blog post.Really thank you! Keep writing.
Hurrah! In the end I got a blog from where I be able to in fact obtain useful
data concerning my study and knowledge.
Thanks