1. Bluetooth
One of the foremost broadly used wireless technologies of short-range is Bluetooth. you’ll quickly get Bluetooth apps that provide you wearable technology for pairing up with the smart gadgets. The recently introduced Bluetooth protocol among the IoT protocols is BLE or Bluetooth Low-Energy protocol. it’ll afford the range of conventional Bluetooth in combined with lower power consumption supremacy.

you’ve got to recollect that BLE isn’t designed for transferring large files and can go perfectly with the tiny portions of knowledge . this is often the rationale for Bluetooth leading the web of things protocols of this century. The newly invented Bluetooth Core Specification 4.2 adds up one innovative Internet Protocol Support Profile. It permits Bluetooth Smart Sensor to urge access on the web straight via 6LoAPAN.
2. WiFi
For IoT integration, WiFi may be a favored choice consistent with many electronic designers. it’s due to the infrastructure it bears. it’s quick data transfer rates along side the aptitude to regulate an outsized quantity of knowledge .

The widespread WiFi standard 802.11 presents you the power to transfer many megabits in just one second. the sole own drawback of this IoT protocol is it can consume excessive power for a few of the IoT Application. It ranges approximately 50 m, and along side performing on internet protocol standards, it includes IoT Cloud infrastructure access. The frequencies are 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
3. ZigBee
a bit like Bluetooth, there’s a huge user base of ZigBee. Among the web of things protocols, ZigBee is meant more for the industrials and fewer for the consumers. it always operates at a frequency of two .4GHz. this is often ideal for the economic sites where data is usually transferred over small rates amongst home or a building.

Recommended Post: Top 20 Emerging IoT Trends which will Shape Your Future Soon
ZigBee and therefore the popular ZigBee remote are popular as famed IoT Security Protocols for supplying secure, low-power, scalable solutions along side high node counts. The ZigBee 3.0 has taken the protocol to one standard. It made it handier.
4. MQTT IoT
MQTT IoT may be a message protocol and full form is Message Queue Telemetry Transport. It developed in 1999 by Arlen Nipper (Arcom) and Andy Stanford-Clark (IBM.) this is often mostly used for monitoring from a foreign area in IoT. The principal task that MQTT does is obtaining data from numerous electrical devices.
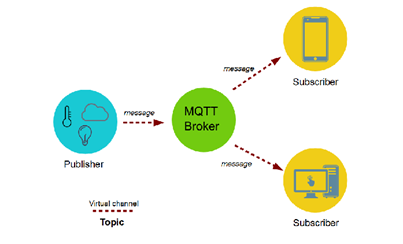
It also conveys them to the IT communications or infrastructure. A hub-and-spoke architecture is fundamentally ordinary for MQTT IoT Protocol. It works on top of the TCP for supplying reliable yet simple streams of knowledge .
This MQTT protocol is formed of three core components or mechanisms: Subscriber, Publisher, and Broker. The work of the publisher is generating data and transmitting the info to the subscriber with the assistance of the broker. Ensuring security is that the job of the broker. It does it by checking and rechecking the authorization of the subscribers and therefore the publishers.
This protocol may be a preferred option for all devices that are IoT based, and these also are capable of providing enough information-routing functions to a budget , low-memory power-consuming and little devices with the assistance of low and vulnerable bandwidth based network.
5. CoAP
The CoAP or Constrained Application Protocol, an online productivity and utility protocol, is especially developed for the restricted smart gadgets. the planning of CoAP is for using it among the devices that have a uniform restricted community. It includes general nodes and devices on the web and different restrained networks and devices that are joined on the web .

IoT systems supported the HTTP protocols can go tremendously with CoAP IoT Network Protocols. It uses the protocol-UDP for implementation of lightweight data. a bit like the HTTP, it also uses the restful architecture. it’s also used inside the mobiles and therefore the other social communities that are basic programs. CoAP helps in getting obviate ambiguity through HTTP get, put up, delete and placed strategies.
6. DDS
Amongst the web of things protocols, the IoT Messaging Protocols – DDS or Data Distribution Service may be a standard for high-performance, expandable and real-time machine-to-machine communication. the info Distribution Service – DDA is developed and designed by OMG or Object Management Group. With the assistance of DDS, you’ll transfer data both within the low-footprint devices and with the Cloud platforms.
the info Distribution Service includes two significant layers. Those are the DCPS and therefore the DLRL. The DCPS or Data-Centric Publish-Subscribe works by delivering information to the subscribers. The DLRL or Data-Local Reconstruction Layer does its job by providing an interface to the Data-Centric Public-Subscribe functionalities.
7. NFC
NFC from the IoT Protocols takes the advantage of safe two-way communication linking. Recently, we saw that the NFC IoT Communication Protocols are applicable for the smartphones.

The NFC or Near Field Communication allows the clients to attach to the electronic devices, to use digital contents and to try to to the contactless payment transaction. The essential work of NFC is to expand the “contactless” card technology. It works within 4cm (between devices) by enabling the devices for sharing information.
8. Cellular
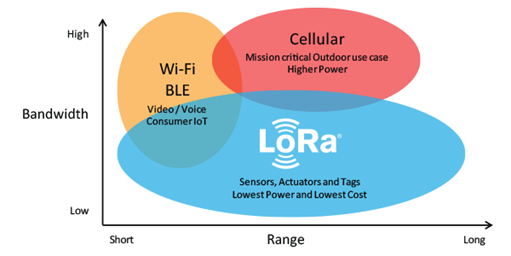
There are tons of IoT applications which will involve operation over a extended remoteness. These IoT applications can take the assistance of Cellular communication capabilities like GSM/3G/4G. Cellular is one among the IoT Communication Protocols which may send or transfer a high amount of knowledge . Here, you’ve got to recollect is that the cost.
The fee for sending a high quantity of knowledge are going to be high too. Cellular does needn’t only high cost but also to wish high power consumption for several applications. This Internet of Things Protocol is amazing for sensor-based data projects of low-bandwidth. this is often because they will send a really insignificant amount of knowledge or information on the web .
It includes the low-cost development board of authentic tiny CELLv1.0. It also features a range of shield that connects boards (so that you simply can use them with the Arduino and Raspberry Pi platforms.) Here, the key product is SparqEE.
9. AMQP
Advanced Message Queuing Protocol or AMQP is an application layer protocol. it’s basically message oriented and designed for middleware environments. The AMQP IoT messaging protocols got the approval as a world standard. The processing chain of AMQP IoT Protocol consists of three necessary components, and people are Exchange, Message Queue and Binding.

The Exchange part works by getting the message and putting them within the queues. the work of the Message Queue is to store the message, and it stores the knowledge until the messages are developed by the client app safely. The work, the Binding Component, does is stating the connection between the Exchange Component and therefore the Message Queue Component.
10. LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN or the Long Ranged Wide Area Network is one among the IoT Protocols for the wide area networks. LoRaWAN IoT Network Protocols is specifically designed for supporting the vast networks with the assistance of million low-power devices. Smart cities use this type of protocol.

Including the low-cost mobile communication, LoRaWAN is additionally famed in many industries for protected bi-directional communication. The frequency of LoRaWAN may vary from network to network. the info rates of this Internet of Things Protocols runs between 0.3-50 kbps. within the urban areas, the range LoRaWAN varies from 2 km to five km. within the suburban areas, the range of this IoT protocol is about 15 km.
Conclusion
There are multiple protocols for IoT but we need to understand first our requirement then we can decide. I will cover each protocol in detail in my next blog.
—


