A wide sort of IoT connectivity standards are already available within the market. generally , standards vary in their technical specifications, which determine the precise IoT use cases which will be served by any particular connectivity solution. a number of these specifications are:
• Frequency
• Max data throughput (data rates)
• Latency
• Battery life in connectivity modules
• Manufacturing costs of connectivity modules
• Maximum data range
• Coverage
• Mobility
• Security
• Scalability (Mesh Network Availability etc.)
• Robustness
• Mobility
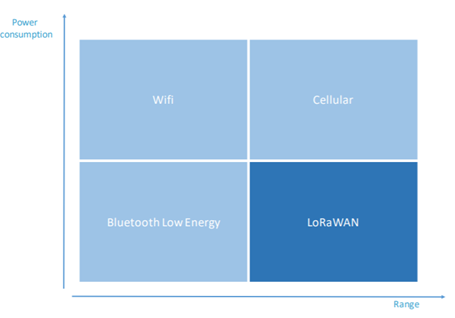
What is LPWAN?
As the name implies, Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs) leave low power consumption over a good area, aka long range. So how is that this accomplished?
Messages sent over LPWAN must be small and straightforward . due to their simplicity, these messages are often communicated over the space without an outsized power source. For machines, decreasing the quantity of knowledge sent (the bandwidth) means lower energy at range.
This is what LPWANs do, they send and receive small packets of data at infrequent intervals. Sensor/devices can send data over miles of range rather than feet and may last for years on battery rather than weeks or months.
However, LPWANs aren’t without downsides. Messages that are transmitted over LPWAN sometimes aren’t received by the gateway (called packet loss). this will usually be overcome by sending multiple messages or by adding additional gateways to the network, but these solutions have power and financial costs respectively.
Despite certain disadvantages, LPWANs play an important role within the Internet of Things.
LPWAN technology thus plays an important role in enabling the web of Things. These networks make it possible to possess many thousands of sensors/devices collecting and sending data at lower cost, over longer range, and with better battery life than other connectivity options. Some use cases among many include:
Two samples of LPWAN implementations are LoRa and Sigfox. While both solutions believe mobile network operators to adopt the technology and implement it across geographies, they need very different business models.
LoRa’s approach means even crowdsourced networks are possible, with lower cost gateways and a reach of a couple of kilometers. this is often possible because LoRaWAN isn’t a corporation , but a typical maintained by the non-profit LoRa Alliance. Each of the businesses within the alliance profit in how from having an open standard for IoT applications, and therefore the LoRa Alliance promotes this standard to urge the various developers and corporations on board. Implementation examples are KPN within the Netherlands, Orange in France, and Digimondo in Germany.
What is LoRa?
LoRa (Long Range) may be a patented digital wireless digital communication IoT technology developed by Cycleo of Grenoble, France. it had been acquired by Semtech in 2012, which holds the IP for LoRa transmission methodology.
LoRa is that the physical layer or the wireless modulation scheme utilized to make long distance communication link Derivative of Chirp Spread Spectrum. Lora is meant for long range, low power, low rate . It support star (not mesh or p2p).
The technology is presented in two parts — LoRa, the physical layer, and; the communication protocol built upon the underlying LoRa physical layer. The communication layer could also be LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network), an open source communication protocol defined by the LoRa Alliance consortium; or could also be Symphony Link, another open source communication protocol defined by a corporation called Link Labs.
LoRa – The Technology behind LoRaWAN
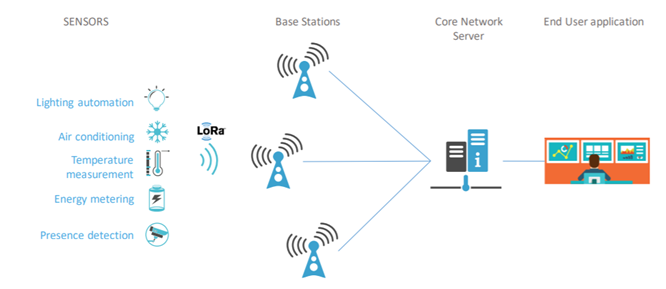
LoRaWAN networks are typically laid out as “star-of-stars” topology during which gateways relay messages between end-devices and a central core network server. All gateways are connected to the core network server via standard IP connections while end-devices use single-hop LoRa™ communication to at least one or many gateways. All communication is natively bi-directional, although uplink communication from an end-device to the network server is predicted to be the predominant use case and traffic patern.
A star specification provides the simplest compromise between long range communication, number of antennas (base stations) and devices battery life.
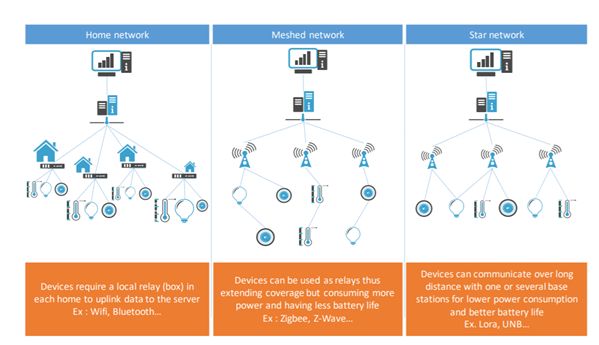
This is a really good image I even have found from Orange Document.
LoRaWAN uses licence-free spectrum, usually ISM (Industrial, Scientific, Medical) bands to speak over the air. In Europe, ETSI regulates the ISM band access on the 868 MHz and 433 MHz bands. The usage of those bands is submitted to limitations: The output power (EIRP) of the transmitter shall not exceed 14 dBm or 25 mW, and therefore the duty cycle imposed in Europe by ETSI is restricted to a quarter (for devices) or 10% (for gateways) counting on the used sub-band.
LoRa enables very-long-range transmissions (more than 10 km in rural areas) with low power consumption.
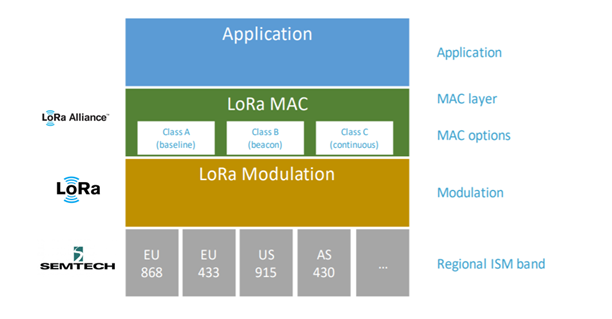
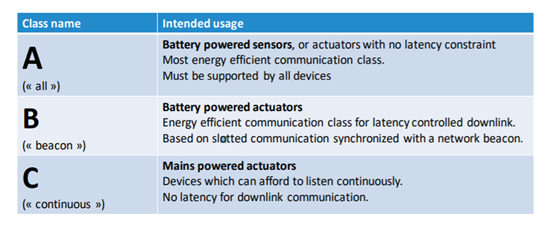
Three different classes (A,B,C) of communication profiles are available in LoRa networks between devices and applications. Each class serves different application needs and has optimized requirements for specific purposes. The key difference between A, B and C profiles is that the trade-off made between latency and power consumption.

Lora Alliance
Gateways
The LoRa sensors transmit data to the LoRa gateways. The LoRa gateways connect to the internet via the standard IP protocol and transmit the data received from the LoRa embedded sensors to the Internet i.e. a network, server or cloud.
The Gateways devices are always connected to a power source. The Gateways connect to the network server via standard IP connections and act as a transparent bridge, simply converting RF packets to IP packets and vice versa.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LoRaWAN
Advantages of LoRaWAN
- Low Powered sensors, and wide coverage area measured in kilometers
- Operates on free(unlicensed) frequencies, no upfront licensing cost to use the technology
- Low power means long battery life for devices. Sensor batteries can last for 2–5 years (Class A and Class B)
- Single LoRa Gateway device is designed to take care of thousands of end devices or nodes
- It is easy to deploy due to its simple architecture
- It is widely used for M2M/IoT applications
- Better payload size (100 bytes), compared to SigFox which is 12 bytes
- Open: an open alliance and an open standard. Open technology compared to competitor SigFox
- No restriction in maximum number of daily messages (compared to SigFox limitation of 140/day)
- LoRaWAN has the benefit of being an alliance with an Open approach instead of a proprietary one (SigFox).
- Long range enables solutions such as smart city applications.
- Low bandwith makes it ideal for practical IoT deployments with less data and/or with data transmissions which aren’t constant.
- Low(er) connectivity costs.
- Wireless, easy to set up and fast deployment.
- Security: a layer of security for the network and one for the application with AES encryption.
- Fully bi-directional communication.
- Backed by the likes of CISCO, IBM and 500 other member companies of the LoRa Alliance.
Disadvantages of LoRaWAN
- Not for large data payloads, payload limited to 100 bytes.
- Not for continuous monitoring (except Class C devices).
- Not ideal candidate for real time applications requiring lower latency and bounded jitter requirements.
- Densification of LoRaWAN networks: The proliferation of LPWAN technologies, and particularly LoRaWAN, poses co-existence challenges as the deployment of gateways populate urban areas.
- Disadvantage of open frequency is that you may get interference on that frequency and the data rate may be low. (For GSM or licensed frequency you can transmit on that frequency without any interference. GSM operators that use certain frequencies pay a large licensing fee to the government for the use of those frequencies. LoRa operates on frequencies that are open and do not need a state license. Keep in mind though that the open frequencies are different from country to country).
References:
It’s important to note that LPWAN is a general term, and there are many different competing standards and technologies under that umbrella. The competing LPWAN standards and technologies include but are not limited to: LoRa, SIGFOX, Ingenu, Weightless, and SymphonyLink.
—



Czlowiek, ktlry w wieku piecdziesieciu lat widzi swiat tak samo, jak widzial go majac dwadziescia lat, zmarnowal trzydziesci lat zycia. – Muhammad Ali