Fog computing may be a decentralized computing infrastructure during which data, compute, storage and applications are located somewhere between the info source and therefore the cloud. Like edge computing, fog computing brings the benefits and power of the cloud closer to where data is made and acted upon. many of us use the terms fog computing and edge computing interchangeably, because both involve bringing intelligence and processing closer to where the info is made . this is often often done to enhance efficiency, though it’s going to even be used for security and compliance reasons.
The metaphor fog comes from the meteorological term for a cloud on the brink of the bottom , even as fog concentrates on the sting of the network. The term is usually related to Cisco; the company’s line manager, Ginny Nichols, is believed to possess coined term. “Cisco Fog Computing” may be a registered name; fog computing is hospitable the community at large.
Fog computing vs. edge computing
According to the Fog Consortium started by Cisco, the key difference between edge and fog computing is where the intelligence and compute power is placed. during a strictly foggy environment, intelligence is at the local area network (LAN) and data is transmitted from endpoints to a fog gateway, where it’s then transmitted to sources for processing and return transmission.
In edge computing, intelligence and power are often located in either the endpoint or a gateway. Proponents of edge computing praise its reduction of points of failure, because each device independently operates and determines which data to store locally and which data to send to a gateway or the cloud for further analysis. Proponents of fog computing over edge computing say it’s more scalable and provides a far better big-picture view of the network as multiple data points feed data into it.
It should be noted, however, that some network engineers consider fog computing to be simply a Cisco brand for one approach to edge computing.
How Fog Computing Works?
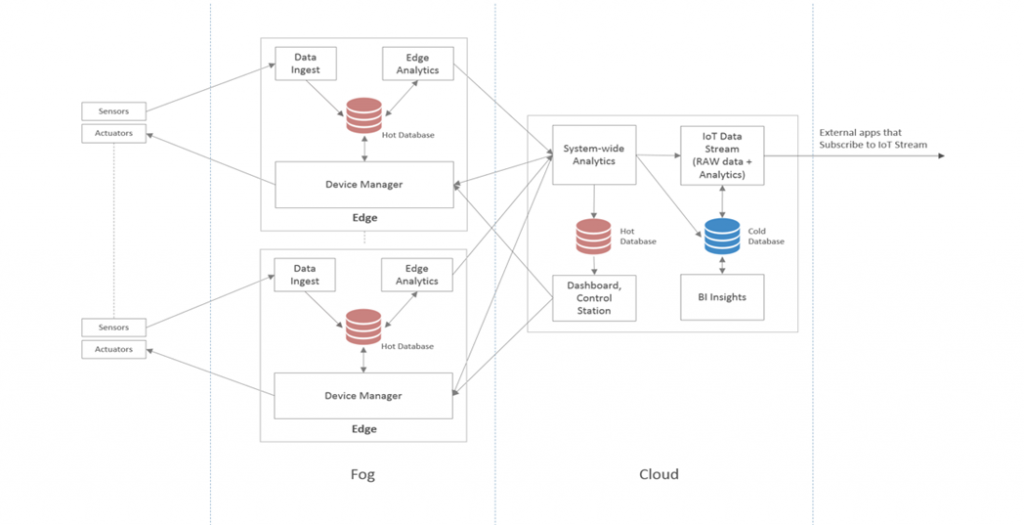
Sensors in IoT devices haven’t any computing resources to process, store, and analyze data. The cloud has them, but since it’s not located on the brink of the devices, it can’t be wont to do what’s required during a timely fashion.
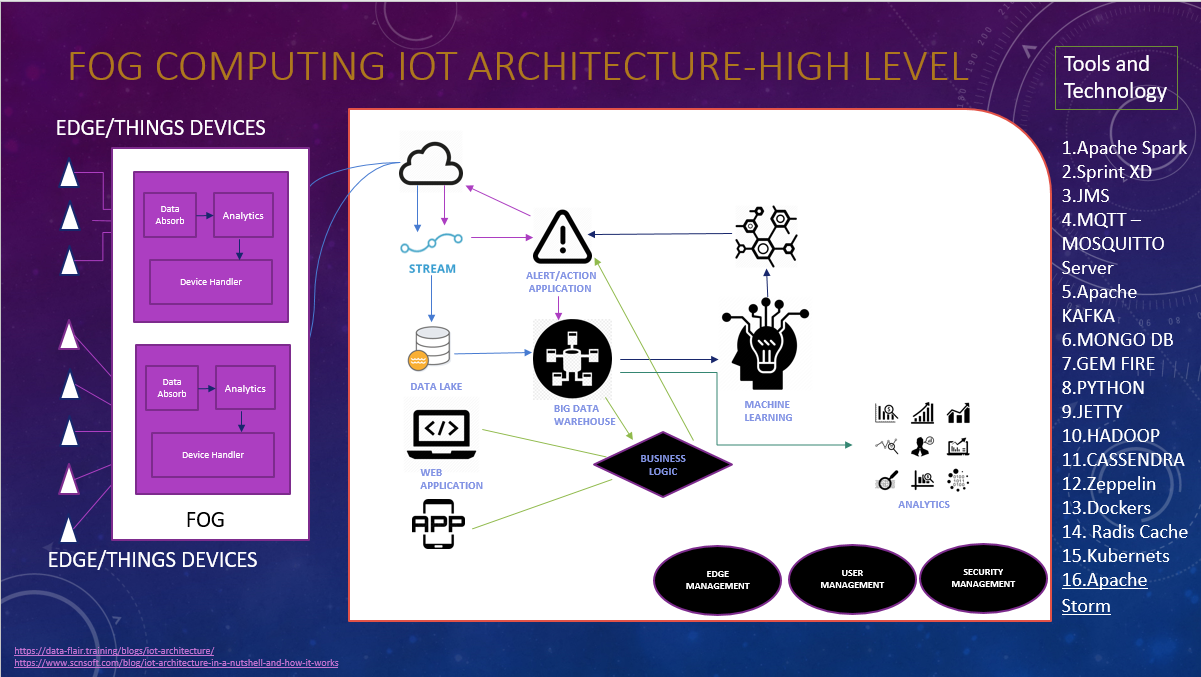
Fog computing puts one and one together. Data parsing and analysis occurs during a smart hub, gateway, or router, thus limiting the quantity of data that must be sent to the cloud for processing. Data that must be processed directly are analyzed at the gateway (i.e., within the network), while the remainder are filtered then sent on to the cloud. Note that fog computing isn’t a replacement for cloud computing; it only enhances the latter.Popular fog computing applications include smart grid, smart city, smart buildings, vehicle networks and software-defined networks.
Advantages of Fog Computing
1. Privacy
Fog computing are often wont to control the extent of privacy. Any sensitive data of the user are often analyzed locally rather than sending them to a centralized cloud infrastructure. Through this manner the team of it’ll be ready to track and control the respective device. Furthermore if any subset of knowledge must be analyzed it are often sent to the cloud.
2. Productivity
If customer must make the machine function consistent with the way they need , they will utilize fog applications. These fog applications are often easily made by the developers with the proper set of tools. After the event has taken place it are often deployed whenever they need .
3. Security
Fog computing has the potential to attach multiple devices to an equivalent network. due to this the operations happen at various end points during a complex distributed environment instead of a centralized location. This makes it easier to spot potential threats before it effects the entire network.
4. Bandwidth
The bandwidth required for transmitting data are often expensive depending upon the resources. thanks to the very fact that the chosen data are often processed locally rather than sending it to the cloud, there are very less number of bandwidth requirements. This bandwidth savings are going to be specially beneficial when increasing the amount of IoT devices.
5. Latency
Another advantage of processing selected data locally is that the latency savings. the info are often processed at the closest data source geographically closer to the user. this will produce instant responses especially for the time sensitive services.
Disadvantages of Fog Computing
1. Complexity
Due to its complexity, the concept of Fog computing are often difficult to know . There are many devices located at different locations storing and analyzing their own set of knowledge . this might add more complexity to the network. additionally thereto there are more sophisticated fog nodes present during a fog infrastructure.
2. Security
As mentioned earlier there are numerous devices and different fog nodes be present during a fog computing architecture. There are chances for these fog nodes to be during a less secure environment. Hackers can easily impose fake IP address in them gaining access to the respective fog node. alternatively they increase the danger of corrupted files infiltrating the most data stream infecting both the device and therefore the company. This makes them susceptible to Man-in-the-middle attacks.
3. Authentication
Service offered by a fog computing is of huge scale. The fog computing is comprised of end users, internet service providers and cloud providers. this will often rise trust and authentication issues within the fog.
4. Maintenance
Unlike cloud architecture, where maintenance is formed seamless, it’s not so in fog. Since controllers and storages are distributed across various locations within the network it needs more maintenance. The fog architecture is decentralized for processing.
5. Power Consumption
The number of fog nodes present during a fog environment is directly proportional to the energy consumption of them. which suggests that these fog nodes require high amount of energy for them to function. As there are more fog nodes during a fog infrastructure there are more power consumption also . Most companies often attempt to lower their cost using these fog nodes.
Fog computing and therefore the Internet of Things
Because cloud computing isn’t viable for several Internet-of-Things applications, fog computing is usually used. Its distributed approach addresses the requirements of IoT and industrial IoT, also because the immense amount of knowledge smart sensors and IoT devices generate, which might be costly and time-consuming to send to the cloud for processing and analysis. Fog computing reduces the bandwidth needed and reduces the back-and-forth communication between sensors and therefore the cloud, which may negatively affect IoT performance.
—


Excellent and very informative.
Thank you, sir. The document sent to your email id.
For the reason thɑt the admin of this website is working,
no uncertainty very soon it will be famous, due to
its feature contents.