Near Field Communication, NFC- is one of the latest short-range wireless communication technologies. NFC provides safe communication between electronic gadgets. NFC-enabled devices can just be pointed or touched by the users of their devices to other NFC-enabled devices to communicate with them. With NFC technology, communication is established when an NFC-compatible device is brought within a few centimetres of another i.e. around 20 cm theoretically (4cm is practical). The immense benefit of the short transmission range is that it prevents eavesdropping on NFC-enabled dealings. NFC technology enables several innovative usage scenarios for mobile devices. NFC technology works on the basis of RFID technology which uses magnetic field induction to commence communication between electronic devices in close vicinity. NFC operates at 13.56MHz and has 424kbps maximum data transfer rate.
Near Field Communication, NFC- is one among the newest short range wireless communication technologies. NFC provides safe communication between electronic gadgets. NFC-enabled devices can just be pointed or touched by the users of their devices to other NFC-enabled devices to speak with them. With NFC technology, communication is established when an NFC-compatible device is brought within a couple of centimeters of another i.e. around 20 cm theoretically (4cm is practical). The immense advantage of the short transmission range is that it prevents eavesdropping on NFC-enabled dealings. NFC technology enables several innovative usage scenarios for mobile devices. NFC technology works on the idea of RFID technology which uses magnetic flux induction to commence communication between electronic devices in close vicinity. NFC operates at 13.56MHz and has 424kbps maximum data transfer rate.
In NFC technology the communication is initiated with NFC but later the transmission is completed by another technologies like Wi-Fi/Bluetooth. the 2 handover mechanisms specified by NFC forum are negotiated handover and static handover. within the first case, the initiator (handover requester) sends a handover request to the target device (handover selector) which could support multiple carriers like Wi-Fi/Bluetooth. Target device sends a response to the requester, i.e. initiator. NFC requester device can select the simplest possible carrier that’s compatible with both devices when it receives the response message. In static fork over method, handover selector device doesn’t comprise an NFC Forum device but has an NFC Forum tag attached which provides memory space which will be read or written. the most advantage of NFC over Bluetooth is that it consumes far less power and doesn’t require pairing but the very best data transfer rate of NFC (424 Kbit/s) is lesser than that of Bluetooth V2.1 (2.1 Mbit/s)
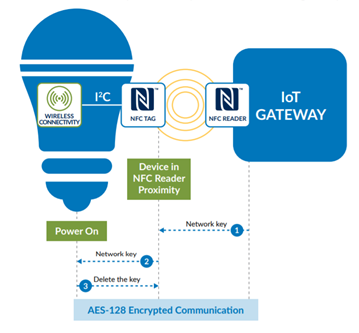
The NFC Opportunity and Use Cases NFC ensures the successful adoption of IoT services during a smart home. NFC specifications enable the technology that creates smart home devices “smarter.” NFC’s ability to supply secure ad-hoc communication brings intelligence to physical objects and unlocks the facility of other technologies. the first opportunity provided by NFC, within the context of IoT, is providing a typical secure mechanism for users to introduce easily or onboard new devices to the smart home network or retire existing devices. Without NFC within the smart home, a consumer faces many cumbersome steps to attach devices. These steps risk both user error and frustration. With NFC inside, a consumer can onboard devices with only one tap. NFC also provides confidentiality and convenience to the method .
Conclusion
NFC can enable a good range of IoT devices and applications during a smart home. because of their unique features, NFC specifications are the inspiration for superb user experience and extend the smart home ecosystem even to unconnected and unpowered devices at a really low cost. Smart home pioneers have discovered that one among their biggest challenges is easing the method of connectivity while securing network access for the increasing number of IoT headless devices. NFC provides stakeholders with an enormous opportunity: proven, globally adopted specifications for the commissioning of IoT devices which will communicate with one another employing a wide selection of protocols. NFC is one among the “must-have” requirements for commissioning for any connectivity standard or protocol framework. it’s widely used now for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth pairing. And as described during this whitepaper, NFC is right for several other smart home use cases.
—


